Gomathi Rajendiran, Mahendran Chinnamuthu, Dr. Deepika Malik Dr. Virendra Bhandari Department of Radiation Oncology , Sri Aurobindo Institute of Medical Sciences, Indore, India
1. INTRODUCTION
The Halcyon V3.0 (Varian Medical Systems) became clinically available in mid-2019, offering key upgrades over V2.0: a. kV imaging capability b. Maximum treatment length of 38.5 cm via multiple isocenters c.0.5 cm MLC resolutionand d. Dynamic beam flattening for 3D conformal planning. Our center installed Halcyon V3.0 in July 2023, among the first in Madhya Pradesh. Hardware, beam data/modeling, and MLC mechanical features remain as in V2.0, with fast IMRT/VMAT delivery (4 RPM, 800 MU/min, 6-FFF beam) and mandatory daily IGRT. The Halcyon uses a preconfigured reference beam model that cannot be altered by the user, making MLC dosimetry and small-field commissioning critical. Published data show good agreement between planned and delivered doses on V3.0. Because the field size is limited to 28×28 cm² , larger targets are treated using a multi-isocenter approach. Eclipse v17.0 uses auto-feathering to blend junction doses, avoiding hot/cold spots.
Integrated EPID with CBCT allows default in-vivo portal dosimetry without extra hardware. QA follows device-based pretreatment checks (3%/3 mm gamma). CBCT is performed daily to minimize setup error, while portal dosimetry verifies delivery accuracy. Multi-isocenter VMAT is valuable for CSI, gynecologic, and extended-field treatments, providing better PTV conformity and organ sparing than older techniques. This study reports our early clinical experience with Halcyon V3.0 for CSI patients using multi-isocenter VMAT and integrated in-vivo dosimetry.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS:
CSI patients were treated on Varian Halcyon V3.0 using extended-field VMAT. Plans were created in Eclipse V17.0 and delivery records with in-vivo portal dosimetry were retrospectively reviewed [1&2].Dose Prescription: 36 Gy in 20 fractions. Immobilization: two orfit masks, arms down, AOI board with headrest, head-first supine. Planning CT (Philips) performed with reproducible setup instructions.
Target length: 75 cm, covered with five isocenters (≤10.5 cm separation, total length 38.5 cm). A single composite plan (12 arcs) (Fig.1) was split into: Upper Plan (2 iso, 5 arcs), Mid Plan (2 iso, 4 arcs), Lower Plan (1 iso, 3 arcs). Daily kV-CBCT was done at a fixed imaging isocenter. Collimators (30°/330°) adjusted for conformity and OAR sparing (Table 2). Goals: D95% ≥ 95%, Dmax ≤ 107.7%, OAR limits per Table 3. Auto-feathering enabled in VMAT optimization. Halcyon DMI: 1280×1280 pixels, 0.34 mm/pixel (panel), 0.22 mm/pixel (isocenter), 43×43 cm size, 16-bit images, up to 20 fps. Portal dosimetry QA (EPID) used 3%/3 mm gamma, ≥97% pass rate. Predicted and measured portal images were analyzed in a composite plan. Daily exit dose per field was compared with the first fraction’s baseline using 3%/3 mm gamma, ≥95% pass for composite fields.
| OAR | DOSE | OAR | DOSE | OAR | DOSE |
| L. Eye lens | Max 8.13Gy | L. Cochlea | Mean 35.8Gy | Larynx | Mean 11.44Gy |
| R. Eye lens | Max 6.08Gy | R. Cochlea | Mean 32.2Gy | Rectum | Mean 0.42Gy |
| L Optic nerve | Max 26.10Gy | Brainstem | Max 38.13Gy | PenileBulb | Mean 0.21Gy |
| R. Optic nerve | Max 28.33Gy | L. Parotid | Mean 9.55Gy | Kidney R | Mean 3.47Gy |
| Optic Chisam | Max 36.82Gy | R.Parotid | Mean 9.61Gy | Kidney L | Mean 3.89Gy |
| Bladder | Mean 0.62Gy | Pituitary | Mean 35.32Gy | R. Femoral Head | Max 0.4Gy |
| Heart | Mean 5.92Gy | L. Eye | Mean 9.83Gy | R. Femoral Head | Max 0.4Gy |
| Liver | Mean 4.95Gy | R. Eye | Mean 8.67Gy | L. Lung | Mean 5.15Gy |
| Intestine | Mean 6.37Gy | Liver | Mean 4.95Gy | R. Lung | Mean 5.68Gy |
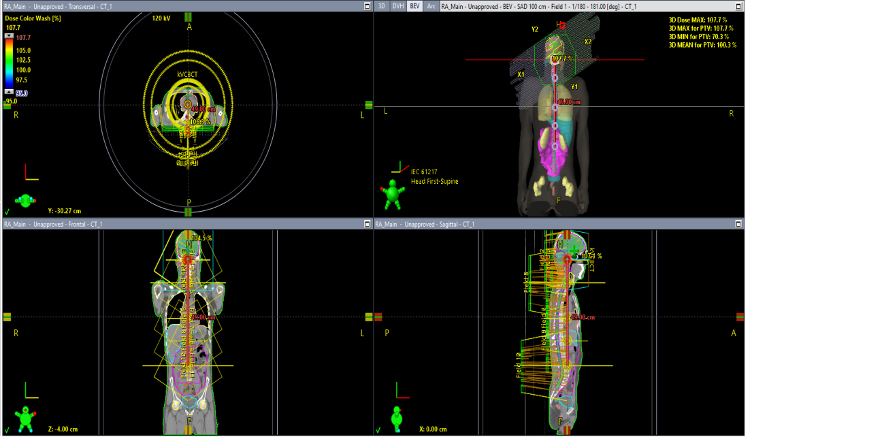
3. RESULT
Multi-isocenter CSI plans met PTV coverage and OAR criteria and were approved by the treating physician. All 20 fractions were delivered as planned.
3.1 Plan Evaluation
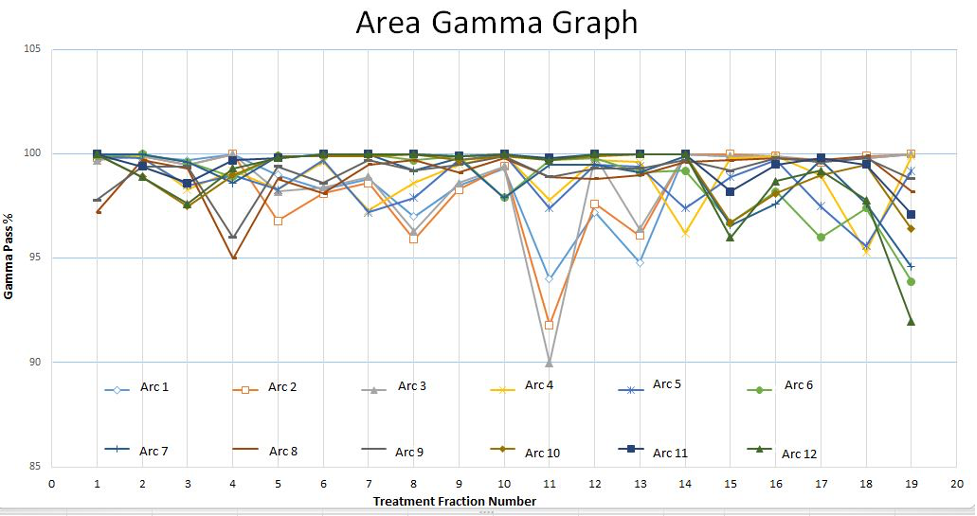
PTV coverage: D95% = 95.46%, HI = 0.11, CI = 1.03. OAR doses: Within institutional criteria; largest deviation occurred in fraction 11, with a 12% gamma area increase due to bowel movement (Fig.2).
3.2 Pretreatment QA
Portal dosimetry gamma analysis:
Mean area gamma = 100% (Tolerance ≥97%)
- Max gamma = 0.79 (Tolerance ≤3)
- Average gamma = 0.14 (Tolerance ≤0.5) 100% pass rate.
3.2 Treatment Delivery & In-Vivo Dosimetry
Daily setup: kV-CBCT (iCBCT) used and avoided MV-CBCT for lower dose and better contrast. Delivery: 12 arcs over 5 isocenters, 10–12 min total time, 1837 MU, 800 MU/min dose rate. Pass rates: 97.3% fractions passed 3%/3 mm gamma criteria (≥95% pixels). Failures: 2 fractions (10%) failed due to bowel filling changes and SSD differences (1.5–2.0 cm).
4. DISCUSSION
This is, to our knowledge, the first report on portal dosimetry using Halcyon V3.0 for multi- isocenter CSI arc planning and delivery. Halcyon V3.0 enables efficient creation of complex arc plans with faster delivery, reducing intra-fraction motion and improving accuracy. The system’s 28×28 cm2 field size limitation is overcome with the multi-isocenter technique, extending the treatment length to 38.5 cm. Auto-feathering ensures homogeneous dose across junctions (Figs. 1).Pretreatment QA using EPID achieved high pass rates, consistent with De Roover et al [3]., and followed AAPM Report 307 recommendations [4]. In-vivo EPID dosimetry showed 97.3% fraction pass rate, with only two failing fractions due to bowel motion and SSD changes (1.5– 2.0 cm). Our findings align with Nailon et al [5]., who reported high in-vivo pass rates across various sites, with deviations mostly due to anatomical changes rather than procedural errors. In CSI, bowel filling/motion is the most variable factor. Treatment delivery was efficient—12 arcs over 5 isocenters in 5–6.5 min—shorter than multi-beam IMRT, with comparable plan quality to C-arm linacs. The recent Eclipse AAA upgrade mitigates prior risks of peripheral hot spots rotational delivery.
5. CONCLUSION
Halcyon V3.0’s multi-isocenter VMAT technique delivers high-quality CSI treatments with integrated in-vivo monitoring. EPID-based dosimetry can identify random anatomical variations, supporting its potential role in adaptive radiotherapy.
References:
- Halcyon System. (Accessed 10/25/2023, at https://www.varian.com/oncology/products/treatment-delivery/halcyon).
- RDS Treatment Planning Instructions for Use Eclipse 15.1.1. Report No.: P1017375‐004‐D.
- De Roover R, Crijns W, Poels K, et al. Validation and IMRT/VMAT delivery quality of a preconfigured fast‐rotating O‐ring linac system. Med Phys. 2019;46:328–339.
- AAPM Report No. 307 – Use of electronic portal imaging devices for pre-treatment and in vivo dosimetry patient-specific IMRT and VMAT QA:(2023) of AAPM Task Group No. 218. Med Phys. 2018;45: e53–e83.
- Nailon WH, Welsh D, McDonald K, et al. EPID‐based in vivo dosimetry using dosimetry check™: overview and clinical experience in a 5‐yr study including breast, lung, prostate, and head and neck cancer patients. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019;20:6–16
